Table of Contents
This page is about the Bahamas geography and climate. It is especially informative for students who want to learn about this fascinating country in the Atlantic Ocean.
This can be particularly helpful if you’re doing a school project or simply curious. This guide includes important facts about Bahamas physical features, climate, and human characteristics.
Where Are the Bahamas?

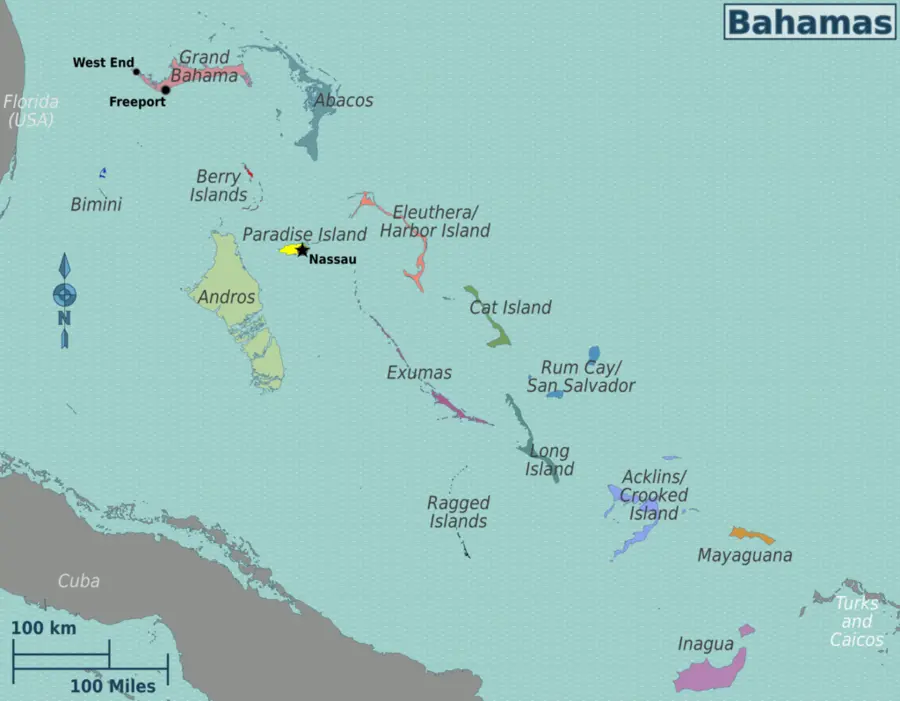
The Bahamas is an archipelago made up of over 700 islands, cays, and islets located in the Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida (USA) and northeast of Cuba. Although only about 30 of these islands are inhabited, the country spreads over 100,000 square miles of ocean.
Fun fact: In 1864, the Governor of the Bahamas reported 29 islands, 661 cays, and 2,387 rocks in the colony!
Bahamas Physical Features
The physical geography of the Bahamas is unique and beautiful. Here’s what stands out:
- All islands are low-lying and relatively flat.
- Some islands have small ridges, which usually rise no more than 15 to 20 meters (49 to 66 feet) above sea level.
- The highest point is Mount Alvernia (formerly known as Como Hill) on Cat Island, which reaches just 63 meters (207 feet).
- The islands are mostly made of limestone, and the surrounding waters are crystal clear with coral reefs, making the Bahamas famous for snorkeling and diving.
Peter Fitzgerald, :wmc:User:NordNordWest, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Bahamas Climate
The climate of the Bahamas is classified as tropical savannah. This means:
- It is warm and sunny year-round.
- There is very little temperature variation — only about an 8°C difference between the hottest and coolest months.
- Summers are hot and humid with more rainfall.
- Winters are mild and drier.
- The Bahamas receives over 3,000 hours of sunlight annually.
Hurricanes in the Bahamas
Like many tropical regions, the Bahamas is vulnerable to tropical storms and hurricanes.
- Hurricane Andrew struck the northern Bahamas in 1992.
- Hurricane Floyd passed near the eastern islands in 1999.
Preparedness and monitoring are very important during hurricane season, which runs from June to November.
Human Characteristics of The Bahamas
The Bahamas is not just about stunning beaches and sunny skies. It has a rich culture and vibrant communities:
- The capital city is Nassau, located on New Providence Island.
- The population is around 400,000 people, most of whom live on New Providence and Grand Bahama Islands.
- The official language is English, making it a key country in any list of English-speaking countries.
- The Bahamas has a mix of African, European, and indigenous Lucayan heritage, which is reflected in its music, festivals, and food.
- Tourism is the main industry, followed by banking and fishing.
The Bahamas Satellite Map
To better understand the geography of the Bahamas, students can explore a Bahamas satellite map, which shows:
- The layout of the islands
- Their proximity to the United States and Cuba
- Clear views of coral reefs, ocean depth, and terrain
These maps are useful in schools and classrooms when learning about island nations.
Quick Bahamas Geography Facts for Students
- 🌍 Region: Atlantic Ocean, near the Caribbean
- 🏝 Number of Islands: Over 700
- 📍 Closest to the U.S.: Bimini Island (known as the Gateway to the Bahamas)
- 🏞 Highest Point: Mount Alvernia, 63 m (207 ft)
- ☀️ Climate: Tropical savannah, hot summers, mild winters
- 🌪 Prone to hurricanes (especially June–November)
- 🗣 Language: English
- 👥 Capital City: Nassau
More about the Bahamas on Wikipedia
FAQs about the Geography of the Bahamas
What is the geography like in the Bahamas?
The geography of the Bahamas is made up of a chain of over 700 low-lying islands, cays, and islets located in the Atlantic Ocean, just southeast of Florida. The islands are mostly flat and made of limestone, surrounded by coral reefs and shallow waters. The landscape is dotted with beaches, mangroves, and small ridges, and the highest point is only 63 meters (207 feet) above sea level. The country covers a wide area, but most of the land is at or just above sea level.
What are the geological features of the Bahamas?
The Bahamas is geologically known for its limestone foundation, which was formed from the remains of marine organisms like coral and shells. Over millions of years, these built up into carbonate platforms. The islands sit on submerged banks, such as the Great Bahama Bank and Little Bahama Bank, with shallow seas and coral reef systems surrounding them. These features make the Bahamas one of the most prominent examples of carbonate island geology in the world.
What are 5 facts about the Bahamas?
Archipelago: The Bahamas includes over 700 islands and 2,000+ cays and rocks.
Flat Landscape: All islands are low and flat, with Mount Alvernia being the highest point at just 63 meters.
Tropical Climate: The Bahamas enjoys a tropical savannah climate, with warm temperatures and lots of sunshine year-round.
English Speaking Country: The official language is English, making it part of the group of English-speaking countries.
Hurricane Zone: The islands are located in the Atlantic hurricane belt and experience tropical storms and hurricanes, especially between June and November.
What is the physical environment in the Bahamas?
The physical environment in the Bahamas consists of coral-based islands, sandy beaches, clear blue waters, and shallow sea banks. The land is generally flat, with very few hills or high elevations. The warm tropical climate, combined with frequent sunshine and occasional hurricanes, shapes the natural surroundings. The islands also feature mangrove forests, coastal wetlands, and underwater caves, making the Bahamas an ecologically rich and delicate environment.
This page about Bahamas geography for students can help better understand how the land, climate, and people shape this beautiful island nation.
The Bahamas is a great topic for geography lessons, from its low limestone landscapes to its sunny skies and rich culture.


